

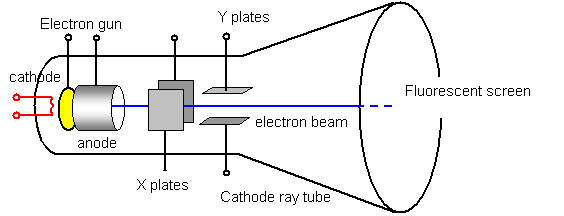
The highly focused beam moves towards vertical and horizontal deflection plates after which it reaches to fluorescent screen.įocusing of an electron beam is accomplished by two different methods- Electrostatic focusing and Electromagnetic focusing. Focusing anode helps in focusing the electron beam and is connected with a lower adjustable voltage of about 500 V. This high positive potential is about 1500 V. The number of electrons emitted from the cathode is controlled by the grid.Ī positive high potential is applied at the pre-accelerating anode by which the beam gets accelerated. The intensity by which beam of electron moves depends entirely on the electron emitted from the cathode. The control grid is basically a nickel cylinder of aperture 0.5. The emitted electrons further pass through a small hole present in the control grid. In the case of a highly efficient system the value is 300 mA at 6.3 V. To obtain high emission of electrons at a moderate temperature a layer of barium and strontium oxide is deposited at the end of the cathode.Īn indirectly heated cathode requires current and voltage value 600 mA at 6.3 V. The cathode is heated indirectly from which electrons are emitted. It consists of a heater, a cathode, pre-accelerating anode, accelerating anode which emits electrons and forms them into a beam. The electron gun is the originator of focused accelerated electron beam. The main parts of CRT are responsible for the working of it that is explained below- Electron gun
CATHODE RAY EXPERIMENT DIAGRAM FREE
The two movements are not dependent on each other that causes the beam to be arranged anywhere on the screen.ĬRT parts are confined in a glass envelope in order to permit free movement of the electron from an end to the other.

This applied voltage enable the beam to move vertically up – down and horizontally from an end to other. The two electrostatic deflection plates deflect the accelerated beam by the application of voltage. This high-velocity beam strikes the fluorescent screen thus causing a luminous spot on the screen. (ii) Isotope of uranium ( 235U) is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors.The diagram given below shows the internal structure of the CRTĪ sharply focused beam is produced by the electron gun assembly. (i) Isotope of cobalt, ( Co), is used in the treatment of cancer. For example, Ne has atomic number as 10 and sodium has atomic number as 11 but both of these have mass numbers as 22. (iv) Isobars are such atoms which have same mass number but different atomic numbers. For example, chlorine has two isotopes with atomic number 17 but mass numbers as 35 and 37. (iii) Isotopes are atoms of the same element thus having same atomic number but different mass number. For example there are 6 protons and 6 neutrons in the nucleus of carbon, so its mass number is 12. (ii) Mass number is defined as the sum of the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. All atoms are characterized by their atomic numbers. For example, there are 6 protons in carbon, so the atomic number of carbon is 6.
(i) Atomic number is defined as number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom. There is a loss or gain in energy of electron when it moves from one orbit to the other. To explain stability of atom and atomic spectra, Bohr suggested that electrons are moving round the nucleus in orbits which have fixed energy shells. This will lead to loss of energy of the moving electron and ultimately giving unstable model of atom. Since charged bodies moving in circular motion emit radiations. Iii)A very small fraction of (a)-particles were deflected by 180 0, indicating that all the positive charge and mass of the gold atom were concentrated in a very small volume with in the atom.ģ.)Neils Bohr. Ii)Very few particles were deflected from their path, indicating that the positive charge of the atom occupies very little space. I)Most of the space inside the atom is empty because most of the (a)-particles passed through the gold foil without getting deflected. On the basis of above experiment Rutherford concluded that: So, the atom as a whole is electrically neutral.Ģ.)Rutherford designed a model in which fast moving alpha (a)-particles were made to fall on a thin gold foil. Ii)The negative and positive charges are equal in magnitude. I)An atom consists of a positively charged sphere and the electrons are embedded in it. On the base of this model Thomson proposed that: In which the positive charge in atom is spread all over like the red edible part of the watermelon, while the electrons are studded in the positively charged sphere, like the seeds in the watermelon. 1).Thomson proposed the model of an atom to be similar to that of a watermelon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
